
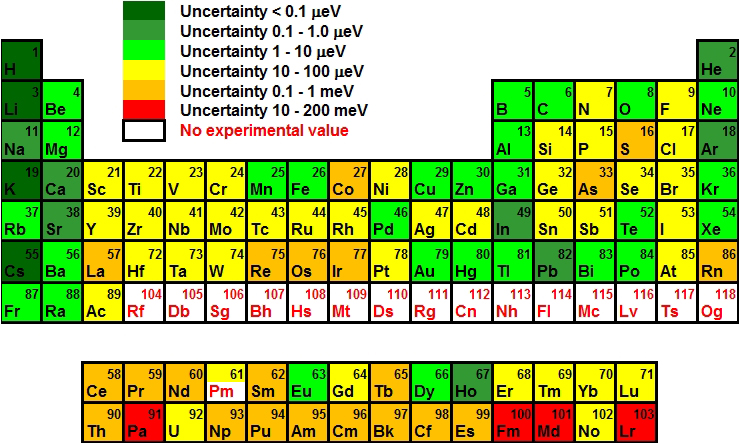
The gain of an electron adds more electrons to the outermost shell which increases the radius because there are now more electrons further away from the nucleus and there are more electrons to pull towards the nucleus so the pull becomes slightly weaker than of the neutral atom and causes an increase in atomic radius. Figure 3: The ionic radius decreases for the generation of positive ions.Īn anion, on the other hand, will be bigger in size than that of the atom it was made from because of a gain of an electron.

A neutral atom X is shown here to have a bond length of 180 pm and then the cation X + is smaller with a bond length of 100 pm. This can similarly be said about the protons pulling the electrons closer to the nucleus, which as a result decreases atomic size.įigure 3 below depicts this process. If ten magnets and ten metallic objects represent a neutral atom where the magnets are protons and the metallic objects are electrons, then removing one metallic object, which is like removing an electron, will cause the magnet to pull the metallic objects closer because of a decrease in number of the metallic objects.

There you can find the metals, semi-conductor(s), non-metal(s), inert noble gas(ses), Halogens, Lanthanoides, Actinoids (rare earth elements) and transition metals.Atomic radius is generally stated as being the total distance from an atom’s nucleus to the outermost orbital of electron. Please note that the elements do not show their natural relation towards each other as in the Periodic system. The oldest chemical element is Phosphorus and the newest element is Hassium. Phone: +31 152 610 900 Chemical elements by discovery yearĬhemical elements listed by the discovery year The chemical elements ofįor chemistry students and teachers: The tabular chart on the right is arranged by the discovery year.Separation and Concentration Purification Request.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
